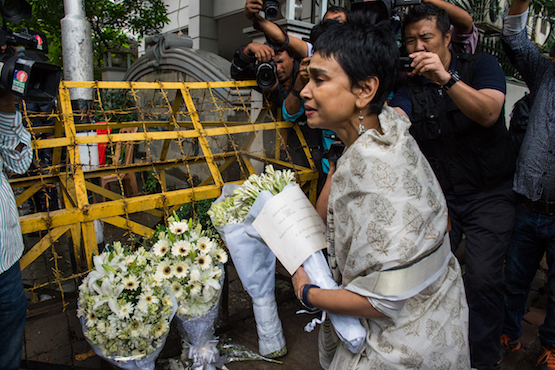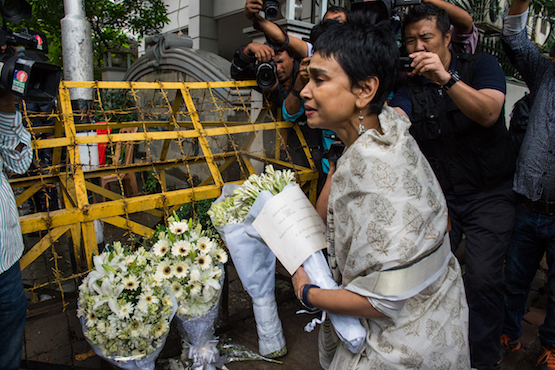 |
| A woman leaves a floral arrangement on a roadblock leading to an upscale cafe in Dhaka on July 3, 2016 that was the site of a bloody siege. (Photo by Roberto Schmidt/AFP) |
Radical outfits such as the so-called Islamic State and Al-Qaeda are exploiting digital communications and the Internet to push disaffected Bangladeshi Muslims into committing terrorist acts.
However, there are concerns that complacency is setting in nearly 14 months after a bloody Islamist siege at a cafe in the capital Dhaka.
Of the 20 people killed, nine were Italian, seven Japanese, one Indian and three Bangladeshi.
And of the five militants who carried out the attack, three hailed from affluent urban families and two came from poor rural backgrounds.
The cafe carnage followed several years' of deteriorating religious and cultural tolerance in Bangladesh.
Since 2013, there have been at least 25 targeted killings by radicals of atheist bloggers, liberal writers, academics, gay and lesbian activists, religious minorities and foreigners.
As with global jihadists, the dream of Bangladeshi militants is to establish an Islamic state.
Attacks, such as the one on the Dhaka cafe, aim to undermine the economy, create political instability and instill fear among liberal Muslims critical of radical Islam.
The government of Bangladesh, concerned the nation could face a Taliban-style insurgency akin to those in Afghanistan and Pakistan, killed 70 alleged militants in a crackdown that lasted until June.
The government ordered that "anti-militancy" sermons be delivered weekly in all mosques. And about 100,000 Islamic clerics issued a fatwa (Islamic ruling) denouncing militancy.
However, that initial energetic campaign to promote communal harmony waned.
Now the pace of anti-extremist action has slowed to mostly sporadic hunts for militants.
A danger is that radicals will make use of the hiatus to re-group and reappear.
Culture of denial still exists
During the past four years, Al-Qaeda-linked groups in Bangladesh have claimed responsibility for killings bloggers, writers, publishers and academics.
Radicals in the country professing allegiance to Islamic State, meanwhile, took credit for attacks on foreigners and religious minorities.
At the beginning, the government sought to portray violent acts as at least partly attributable to opposition political parties trying to 'destabilize' the government.
However, it subsequently conceded that the two main groups involved were Ansarullah Bangla Team (ABT) and the revived militant outfit, Jamaatul Mujahedin Bangladesh (JMB).
The first organization is said to be influenced by Al-Qaeda ideology while the JMB pledges allegiance to Islamic State.
Islamic State and Al-Qaeda don't need to set up bases in Bangladesh to launch attacks. In this digital age, they can influence others to carry out attacks in different parts of the world, including Bangladesh.
Bangladesh has more than eight million expatriate workers spread across the globe and many become radicalized while abroad.
Surprisingly, when militants launched deadly attacks on atheist bloggers and writers, the government rebuked the bloggers for their critical writings instead of protecting them.
This culture of denial still exists.
No holistic approach to counter-terrorism
Bangladesh has no national counter-terrorism strategy that involves 'all of government' and society.
This contrasts with the United States where, following a commission of inquiry into Al-Qaeda's 9/11 attacks of 2001, there was a major counter-terrorism overhaul. That included creation of a special agency, Homeland Security, to overcome rivalry between the FBI and the CIA.
The government of Bangladesh, though, has yet to adopt a highly coordinated approach, not overwhelmingly dependent on the use of force.
The Bangladeshi Mujahidin of Afghan War formed the first batch of Islamic militants in 1990s. A second batch arose from fleeing Taliban operatives after the 2001 U.S. invasion of Afghanistan.
Each time the government responded by using force: arresting and executing extremists. However, they have re-emerged in new forms and with new leaders. Networks were weakened, but not annihilated.
Arguably, the most important step towards combating extremism is to present a 'counter ideology' to those individuals and groups that have already been radicalized. However, there is no such policy in place, even in prisons where radicals are held.
To combat the existential threat posed by militants, there needs to be an alliance between government and concerned sections of the society to develop and implement anti-terrorism policies.
Lack of political consensus
Major political parties — the ruling Awami League and opposition Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP) — are "blood-feud" rivals unable to reach a consensus on important national issues. Even in the wake of the bloody cafe attack, no consensual counter-terrorism strategy was formulated.
The center-right BNP has traditionally had warm relations with some radical Islamist political parties. And the BNP came to power twice — in 1991 and 2001 — through alliances with what have been branded as "political Islamists."
Meanwhile, the avowedly secular Awami League has also been trying to appease radical groups in different ways, including through recognition of religious madrasa educational degrees and the 'Islamizing' of school textbooks.
Cyber radicalism
More needs to be done to combat on-line propaganda, including through social media, by radical groups such as Islamic State and Al-Qaeda. Disgruntled and detached people, often young, can be too easily influenced to become violent.
Instead, in recent years, Bangladeshi authorities have targeted dissidents and government critics. Some on-line articles critical of aspects of religious practice, including Islam, have been removed. Dozens of bloggers, journalists and government critics have been harassed under the Information and Communication Technology Act.
After so much bloodshed, Bangladesh must look to countering extremism with a coordinated, multi-dimensional approach.
END
Click for original piece here